Phonetis: The Sound of American English
Vowels
Monophthongs
Monophthongs are a sound of a single vowel1. Monophthongs - front vowels
A front vowel is produced with a forward shift of the tongue from its neutral or rest position:
/i:/ & /ɪ/, as in eat & pin.
/eɪ/ & /ɛ/, as in eight & extra;
/æ/ , as in at.
2. Monophthongs - central vowels
A central vowel is produced with the tongue in its neutral or rest position:
/ʌ/ & /ə/, as in under & asleep;
/ˈɚ/ & /ɚ/, as in earth & farmer *.
* /ˈɚ/ (in stressed syllable) is the same that /ˈʌr/, and /ɚ/ (in unstressed syllable) is the same that /ər/.
3. Monophthongs - back vowels
A back vowel is produced with a backward shift of the tongue from its neutral or rest position:
/u:/ & /ʊ/, as in drew & foot;
/oʊ/ & /ɔ/, as in over & all (BrE) *;
/ɑ:/ , as in clock or in all (AmE).
* The sound /ɔ/ is short in British English (BrE). In the same words in American English (AmE), the sound /ɔ/ is a long sound colored as /ɑ:/.
Diphthongs
Diphthongs are two vowels produced consecutively in the same syllable by moving the articulators smoothly from the position of one to the other:
/aɪ/ & /aʊ/;
/oɪ/.
Consonants
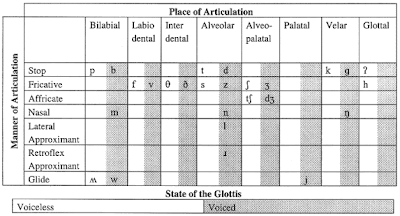
Manner
Manner of articulation refers to how the sound is produced and the way in which the airstream is modified as it passes through the vocal tract.1. Manner - stop
A stop is a consonant characterized by:
(1) complete obstruction of the outgoing aurstream by the articulation,
(2) a build of intraoral air pressure, and
(3) a release.
Stops - voiceless & voiced
/p/ & /b/ (bilabial)
/t/ & /d/ (linguaalveolar)
/k/ & /g/ (linguavelar)
2. Manner - fricative
A fricative is a consonant produced by forcing the breath stream through a constriction formed by articulation in the vocal tract.
Fricatives - voiceless & voiced
/f/ & /v/ (labiodental)
/θ/ & /ð/ (linguadental)
/s/ & /z/ (linguaalveolar)
/ʃ/ & /ʒ/ (linguapalatal)
/h/ & none (glottal)
3. Manner - affricate
An affricate is a consonant characterized as having both a fricative and a stop manner of production.
affricate - voiceless & voiced
/tʃ/ & /dʒ/ (linguaalveolar)
4. Manner - nasal
Nasal refers to a consonant produced with complete closure in the oral cavity along with a lowered velum to allow airflow through the nasal cavity.
Nasal - voiceless & voiced
/m/ (nilabial)
/n/ (linguaalveolar)
/ŋ/ (linguavelar)
5. Manner - liquids
Liquid is a generic label used to classify two English approximant consonants, /r/ and /l/.
Liquids - voiceless & voiced
/l/ (Linguaalveolar)
/r/ (linguapalatal)
6. Manner - glide
A glide is a consonant characterized by a continue, gliding motion of the articulators into the following vowel; also referred to as a semi-vowel, e.g., /j/ and /w/.
Glides - voiceless & voiced
none & /w/ (bilabial)
none & /j/ (linguapalatal)
Place
Place of articulation refers to which articulators are involved in the production of a particular sound.1. Place - bilabial
Bilabial refers to a speech sound, such as /b/ produced by contact of the upper and lower lips.
Bilabial - voiceless & voiced
/p/ & /b/ (stop)
none & /m/ (nasal)
none & /w/ (glide)
2. Place - labio-dental
A labiodental consonant is one that is produced by the lower lip contacting the upper front teeth.
Labio-dental - voiceless & voiced
/f/ & /v/ (fricative)
3. Place - lingua-dental
A linguadental consonant is produced with the tongue contacting the teeth.
Lingua-dental - voiceless & voiced
/θ/ & /ð/ (fricative)
4. Place - lingua-alveolar
Linguaalveolar refers to a consonant produced with the tongue contacting the upper alveolar ridge.
Lingua-alveolar - voiceless & voiced
/t/ & /d/ (stop)
/s/ & /z/ (fricative)
/tʃ/ & /dʒ/ (affricate)
none & /n/ (nasal)
none & /l/ (liquid)
5. Place - lingua-palatal
A linguapalatal consonant is produced with the tongue contacting the hard palate.
Lingua-palatal - voiceless & voiced
/ʃ/ & /ʒ/ (fricative)
none & /r/ (liquid)
none & /j/ (glide)
6. Place - lingua-velar
Linguavelar refers to a consonant produced with the tongue contacting the velum.
Lingua-velar - voiceless & voiced
/k/ & /g/ (stop)
/ŋ/ (nasal)
7. Place - glotal
Glotal is a place of articulation referring to a consonant that is produced by completely or partially constricting the glottis.
Glottal - voiceless & voiced
none & /h/ (fricative)
Voice
Voicing refers to whether the vocal folds are vibrating during a production of a particular consonant.1. Voice - voiced
A voiced sound is produced with vibration of the adducted vocal folds in the larynx.
/b/ & /d/ (stop)
/g/
/v/ & /ð/ (fricative)
/z/ & /ʒ/
/dʒ/ (affricate)
/m/ & /n/ & /ŋ/ (nasal)
/l/ & /r/ (liquid)
/w/ &/j/ (glide)
2. Voice - voiceless
A voiceless sounds are consonants produced without vibration of the vocal folds.
/p/ & /t/ (stop)
/k/
/f/ & /θ/ (fricative)
/s/ & /ʃ/
/h/
/tʃ/ (affricate)
Phonetics: The Sound of American English (1)
Phonetics: The Sound of American English (2)
Phonetics: The Sound of American English (3)


No comments:
Post a Comment
Thank you!